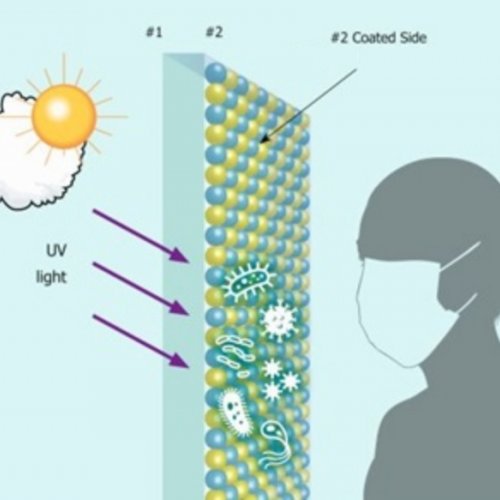
The antimicrobial glass uses a TiO2 based coating deposited directly onto the glass surface during its manufacturing process. When the antimicrobial coating is exposed to UV radiation from natural daylight or from UV disinfection devices it gets activated.
It then reacts with water vapour within the air, in a photocatalytic process that produces reactive oxygen species. These species provide a number of functions, including the ability to break down organic species, providing antimicrobial properties and activity against enveloped viruses on the glass surface.
When the coated glass surface is treated using a UV disinfection process, the effectiveness of disinfection is increased and in some cases doubled, compared to using uncoated glass.
Features & Benefits
- It is a high quality glass with photocatalytic coating that can be used in a large variety of glazing applications;
- It is highly resistant to corrosion, physical force and chemical damage;
- It can be activated by sunlight or by artificial UV irradiation. It is rapidly activated by 254 nm light, the same used by UV disinfection systems;
- It rapidly achieves its full activity upon exposure to UV light – only 5 to 10 minutes of UV exposure is needed;
- It can double the effectiveness of UV disinfection processes;
- Once activated, it retains photocatalytic activity for up to 2 hours, even in the dark;
- When activated, it is also oleophobic (i.e. anti-fingerprint) and easier to clean than regular glass;
- The glass can be toughened, laminated, bent and processed into insulating glass units.
Exterior applications:
- glass facades,
- windows,
- doors,
- external partitions.
Interior applications:
- wall cladding,
- glass screens, barriers and partition walls,
- table tops, counter tops,
- splashbacks,
- furniture,
- freezers and refrigerators,
- cover glass for touch screens/displays