The first glass panes appeared about 2,000 years ago and were used to "close" building openings, providing protection to their occupants from the weather (wind, rain, cold, etc.) while allowing light to enter. This remains the main purpose of glass panes today.
For many centuries, of course, the use of glass in buildings was not widespread, while only in the 20th century began a substantial improvement in the efficiency of glass.
Around the end of the 1940s, the idea of double glazing to improve the thermal insulation of glassworks began to be cultivated, but its real development in Western Europe came with the energy crisis of the 1970s.
Benefiting from the extensive research and development efforts of the last decades, glass, today contributes significantly in all ways, to the comfort level of buildings and especially homes. Advanced types of glass, such as coated, laminated, etc., now provide high quality solutions in areas such as thermal and solar control, sound reduction and safety.
Modern windows are made from float glass. The float glass process is also known as the Pilkington process, named after the British glass manufacturer Pilkington, which pioneered the technique in the 1950s at their production site in St Helens, Merseyside in Great Britain.
Decorative Glasses are determined by the existence of a design or color on them. From their name it is concluded that their main use is the buildings' decoration, such as partitions, furniture, closets, etc.
Mirrors are made when a thin layer of silver, or sometimes aluminium, is coated on the back side of a float glass so that someone can see the surface reflected through the glass. The back of the mirror is usually coated with dark varnish to protect the silver from corrosion and detachment from the float glass. This method reflects about 80% of the incident light.
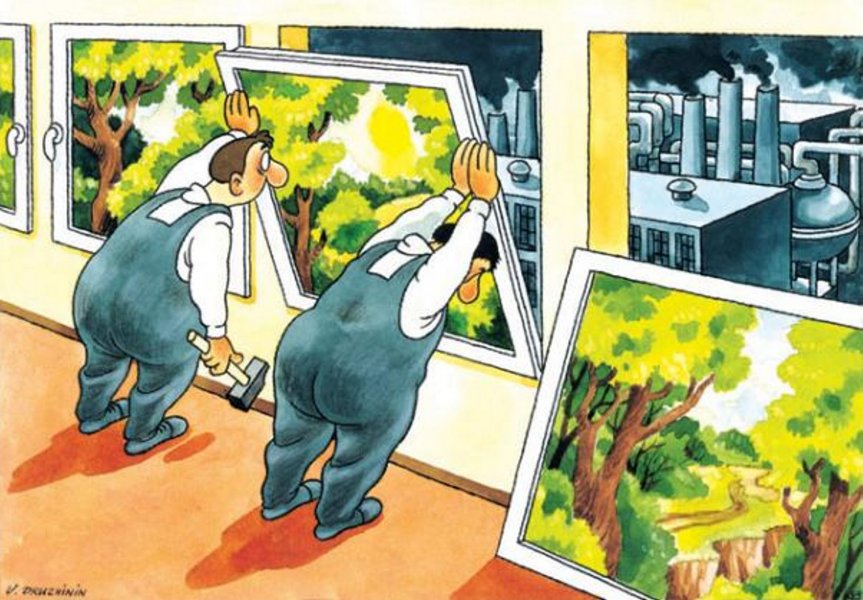
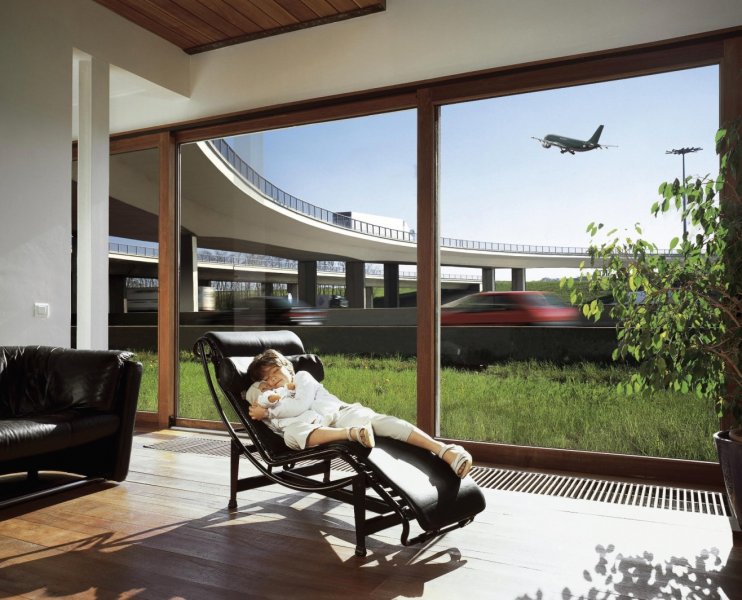
The term “Low-e Glass” in recent years is used as a free translation of the term “Energy efficient glass” to determine that the category of glass, that has characteristics which make it difficult to transfer heat from one side to another, thereby contributing to energy saving.
The invention of these glasses was a revolution in the technology of insulating materials, given their impressive greater insulating performance, compared to all previously known types of glass, 220% better thermal insulation in comparison with standard double glazing and 400% compared with the ordinary single glazing!
In principle, the “Low-e Glasses” have the “ability” of decreasing the emission of heat from the warmer to the cooler side (hence called low emissivity glass “Low-E”). That their ability helps us to save energy (for heating or room air conditioning), as we “keep” the heat of our house in winter and we “through” the heat of the external environment outside in summer.
Nowdays technology and research has enabled the glass industry to develop special coatings applied to glass for applications of high demands and high aesthetics.
The Sound Insulating Glasses have the ability to damp the resonance phenomena, eliminating the phenomena of the “acoustic window”.
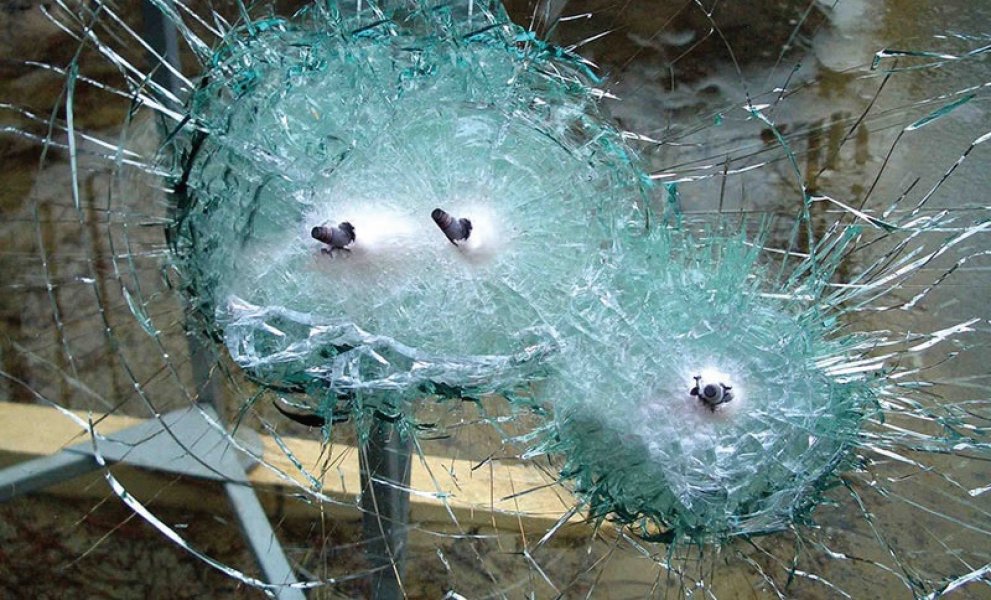
Modern technology succeded to give many safety properties in glass:
- Injury protection
- Protection against vandalism
- Bulletproof
- Missile protection
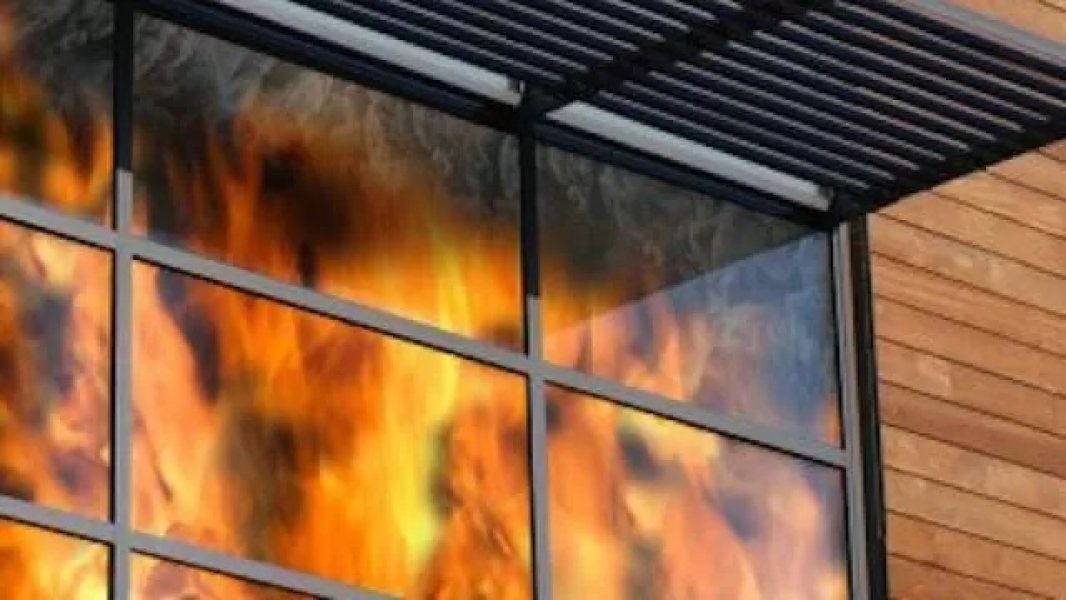
- Fire & tempereture protection